Cat 7 vs. Cat 8: Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable
1.What is Cat7 Ethernet Cable?
Designed for high-speed networks, Cat7 cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps and 600 MHz bandwidth, which is suitable for most home and small office needs.
These cables are shielded to minimize external sources of interference. They typically have individual pair shielding and overall shielding to improve performance in environments with a lot of devices.
Common use cases include home networking and device connectivity in small offices. If you're setting up a gaming or streaming network, Cat7 can provide a reliable connection without too much noise.

2.What is Cat8 Ethernet Cable?
Cat8 cables represent the latest in Ethernet technology. They offer speeds of up to 25-40 Gbps and bandwidths up to 2000 MHz. This high performance is essential for demanding applications.
Similar to Cat7, Cat8 cables also feature robust shielding to minimize interference. This makes them ideal for environments such as data centers and professional equipment.
However, Cat8 has a maximum length of 30 meters, which limits its use in larger spaces. You can see these cables in high-performance computing scenarios, where speed is critical for data transmission and processing.

3. Cat 7 vs. Cat 8: Performance Comparison
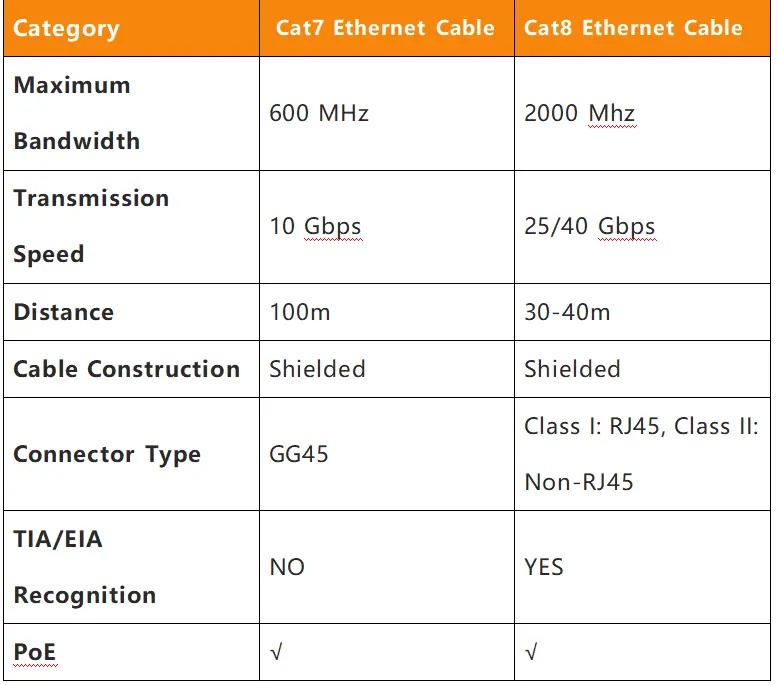
Performance:
The main difference between Cat7 and Cat8 Ethernet cables is speed and frequency. Cat7 has a channel bandwidth of up to 10Gbps at a frequency of 600Mhz; Cat8 has a channel bandwidth of up to 40Gbps at a frequency of 2000Mhz.
Cat8 is recommended for data centers or 25G/40G applications, while Cat7 is recommended for home or office network applications. Both cables are shielded to minimize interference. Although Cat8 outperforms traditional Cat cables over 30 meters of cable, its performance is much higher within the first 30 meters.
If you want a cable that guarantees high speed and performance for several years, you should choose Cat 8. If you want high performance but at a more affordable price, consider Cat7.
Cable Length:
Cat 7 cables can run up to 100 meters without sacrificing speed. However, Cat 8 cables have limitations in terms of distance, and are usually limited to 30 meters to reach their maximum speed.
Shielding:
Both Cat7 and Cat8 cables are shielded to minimize interference. Cat7 has an additional shielding layer to reduce the loss of signal strength (attenuation) as the signal travels through the cable.
However, to get the performance that Cat7 offers, you need to use GigaGate45 connectors. Cat8 cables are also shielded, but perform better, supporting data rates of up to 40 Gbps and up to 30 meters.
Cat7 focuses more on reducing crosstalk, while Cat8 combines shielding and higher bandwidth for more complex connections.
4.Which is better, CAT7 or CAT8?
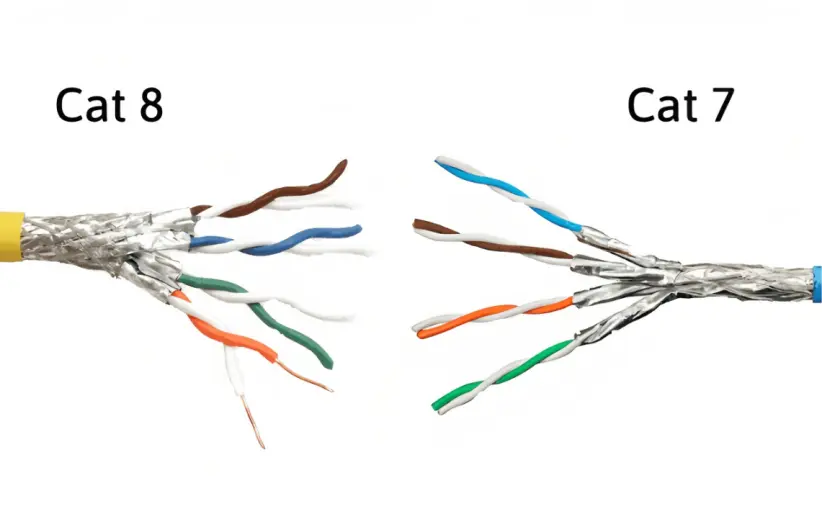
When choosing between Cat7 and Cat8 cables, users often choose the latest model with better performance, but this is not the case. When choosing a network cable, users should evaluate it based on actual needs. Here are some reference factors:
Network needs
If it is a home or small office, CAT7 network cable is sufficient for daily use. If the speed and bandwidth requirements are relatively low, CAT6 or CAT6A network cables can also meet daily network needs. But if large enterprises or data centers have higher performance requirements, CAT8 network cable is undoubtedly a better choice because it can meet the needs of transmitting large amounts of data.
Installation environment
When choosing an Ethernet network cable, you also need to consider the actual wiring environment and distance limitations. For network or Ethernet connection applications not exceeding 30 meters, Cat8 network cables always perform better. But Cat7 network cables can be used for longer distances.
Future scalability
Consider possible future network upgrade needs. If you plan to expand your network in the future, investing in CAT8 network cables may have longer-term value.
Budget
When purchasing a network cable, users may consider budget and cost-effectiveness. Category 8 network cables are generally more expensive than Category 7 network cables, and installation and maintenance are relatively complex. In the actual process, you also need to weigh performance and cost according to the specific situation.

 USB C Docking & Hub
USB C Docking & Hub USB C Docking Station
USB C Docking Station USB C Hub-H Series
USB C Hub-H Series USB C Hub-H Series High End
USB C Hub-H Series High End USB C Hub-X Series High End
USB C Hub-X Series High End HDMI Cable
HDMI Cable 4K HDMI Cable
4K HDMI Cable 8K HDMI Cable
8K HDMI Cable 16K HDMI Cable
16K HDMI Cable AOC HDMI Cable
AOC HDMI Cable HDMI Conversion Cable
HDMI Conversion Cable 8K DisplayPort Cable
8K DisplayPort Cable 16K DisplayPort Cable
16K DisplayPort Cable DisplayPort Conversion Cable
DisplayPort Conversion Cable XLR Cable
XLR Cable VGA Cable
VGA Cable DVI Cable
DVI Cable Type C To HDMI
Type C To HDMI Type C to DP
Type C to DP Type C to DVI
Type C to DVI Type C Adapter
Type C Adapter USB A to C Cable
USB A to C Cable USB C to C Cable
USB C to C Cable Micro USB Cable
Micro USB Cable USB4 Cable
USB4 Cable