DisplayPort Cable
DisplayPort Cable
A DisplayPort is a digital display interface that can link a video source to a display device like a television, monitor, or projector. A standard DisplayPort connector transmits data through DisplayPort through packets instead of a continuous stream. This data transmission is great for higher bandwidth and quick transmission speed, thus perfect for high-resolution displays and multiple monitor setups.

1.Key Features of DisplayPort Cables
- High bandwidth capacity
One of the standout features of DisplayPort technology is its high bandwidth capacity. This enables it to transmit high-resolution video and fast refresh rates, making it ideal for advanced digital displays. Compared to other standards such as HDMI, DisplayPort cables generally offer higher bandwidth, which means better video quality and smoother performance.
- Versatility and compatibility
DisplayPort cables are designed to be flexible and compatible with a wide range of devices. They support a wide range of video formats and resolutions, including 4K and above, to meet the needs of both consumer and professional markets. The standard also ensures backward compatibility, allowing users to connect new DisplayPort devices to older interfaces with the correct adapter.

- Audio and video transmission
DisplayPort cables can transmit audio and video signals over a single cable. This feature simplifies setup and reduces cable clutter, making it a convenient choice for many users. Transmitting high-quality audio at the same time as video is particularly beneficial for gaming, home theater, and professional AV setups.

2.Evolution of the DisplayPort Standard
The DisplayPort standard continues to evolve with additional features and versions to support higher resolutions, higher refresh rates, and other advanced display technologies. The DisplayPort standard has gone through the following versions:
- Displayport 1.0: The original version of DisplayPort was released in 2006, allowing 8-bit color depth and a maximum resolution of 2560 × 1600 pixels at 60 frames per second.
- Displayport 1.1: This version was introduced in 2007 and supports higher color depths (including 10-bit and 12-bit) as well as DisplayPort audio.
- DisplayPort 1.2: This version was released in 2009 and increased the maximum resolution to 3840 x 2160 pixels at 60 frames per second and 10-bit color depth. In addition, it added support for daisy chaining (multiple monitors can be connected together) and multi-stream transmission (multiple monitors can be connected to a single DisplayPort output).
- Displayport 1.3: Released in 2014, this version has a maximum resolution of 7680 x 4320 pixels, a refresh rate of 60 Hz, and a color depth of 10 bits. In addition, it adds support for Display Stream Compression (DSC), which enables higher resolutions and refresh rates over a single DisplayPort connection, as well as High Dynamic Range (HDR) color, which provides a wider range of colors and higher contrast.
- Displayport 1.4: Released in 2016, this version supports 10-bit color depth and HDR, and increases the maximum resolution to 7680 x 4320 pixels at 60 Hz. In addition, it supports forward error correction (FEC) for improved data reliability, and supports multi-stream transport (MST) for daisy-chaining up to four monitors.
- Displayport 2.0: Released in 2019, it has a maximum bandwidth that is three times that of the previous version, enabling higher resolutions and refresh rates. DisplayPort 2.0 has 10-bit color depth and HDR compatibility, supporting a maximum resolution of 7680 x 4320 pixels at 120 Hz.
- DisplayPort 2.1: The latest DisplayPort 2.1 version was released in 2022. It allows a maximum bandwidth of up to 80Gbps (depending on the transmission mode) and is forward compatible with previous DisplayPort standards. DP 2.1 also supports DSC (Display Stream Compression) and MST (Daisy Chain), enabling it to support higher resolutions and refresh rates, such as 4K240Hz, 8K60Hz, etc. With the support of DSC, DP 2.1 can reach a resolution and refresh rate of up to 16K60Hz.
3. Advantages of DisplayPort
DisplayPort offers many advantages over analog interfaces. It supports higher resolutions and refresh rates than VGA, DVI, or HDMI. It also transmits video and audio signals with less compression than any other connection type, making it ideal for gamers who demand the ultimate in image quality and fidelity. It also transmits data faster than other standards, so large files can be transferred faster. Finally, because only one cable is needed to transmit power and audio/video data, DisplayPort requires fewer cables than analog connections, making it ideal for multi-monitor desktop setups.

4. What is DisplayPort used for?
DisplayPort was designed to make it easy to multitask in today's digital world. Using DisplayPort makes it easier to connect multiple monitors, increasing productivity and efficiency. It is passionate about providing the highest performance for gaming PC users, allowing them to experience the full power of today's advanced graphics.


 USB C Docking & Hub
USB C Docking & Hub USB C Docking Station
USB C Docking Station USB C Hub-H Series
USB C Hub-H Series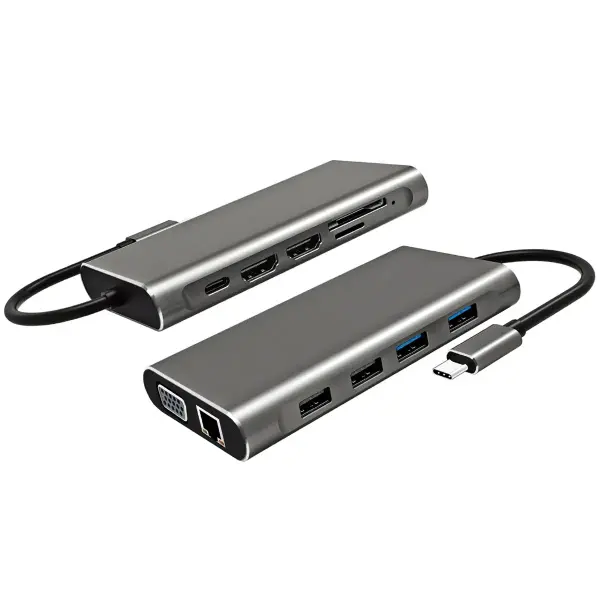 USB C Hub-H Series High End
USB C Hub-H Series High End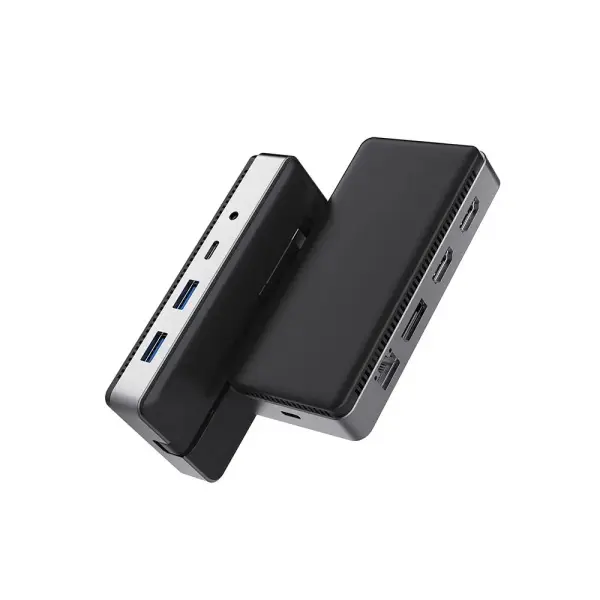 USB C Hub-X Series High End
USB C Hub-X Series High End HDMI Cable
HDMI Cable 4K HDMI Cable
4K HDMI Cable 8K HDMI Cable
8K HDMI Cable 16K HDMI Cable
16K HDMI Cable AOC HDMI Cable
AOC HDMI Cable HDMI Conversion Cable
HDMI Conversion Cable 8K DisplayPort Cable
8K DisplayPort Cable 16K DisplayPort Cable
16K DisplayPort Cable DisplayPort Conversion Cable
DisplayPort Conversion Cable XLR Cable
XLR Cable VGA Cable
VGA Cable DVI Cable
DVI Cable Type C To HDMI
Type C To HDMI Type C to DP
Type C to DP Type C to DVI
Type C to DVI Type C Adapter
Type C Adapter USB A to C Cable
USB A to C Cable USB C to C Cable
USB C to C Cable Micro USB Cable
Micro USB Cable USB4 Cable
USB4 Cable