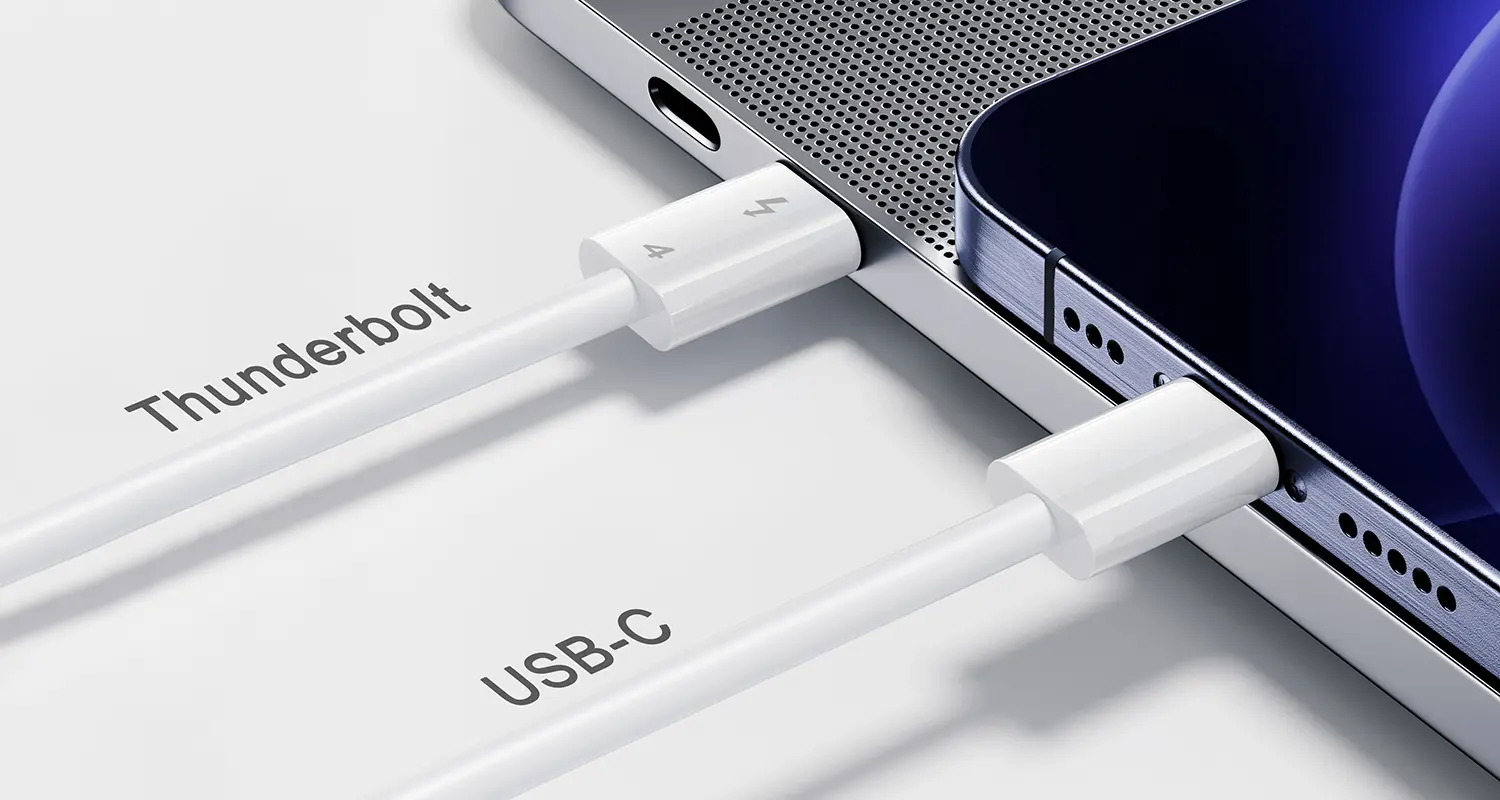
The difference between Thunderbolt and USB-C
Thunderbolt and USB-C are increasingly common on today's digital devices. Many people are confused by these two similar-looking connectors when charging their phones or connecting computer peripherals: Do they function the same way if they look similar? Why are some devices labeled Thunderbolt while others simply say USB-C? While these two connectors are related, they differ significantly. This press release explains the differences between Thunderbolt and USB-C to help you navigate device purchases and daily use.

What is USB-C?
USB-C is the most modern version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard. Its oval shape and convenient connection distinguish it from earlier USB types like USB-A. Unlike its predecessors, USB-C is compact and compatible with smartphones and other small devices. The symmetrical design of the USB-C connector eliminates the need to worry about plug orientation, significantly improving both design and functionality. USB-C is widely used for charging, data transfer, and display connections across a wide range of technological devices, demonstrating its ability to efficiently transmit data and power.
What is Thunderbolt?
Thunderbolt is a technology launched in 2011 by Intel and Apple. It aims to enable high-speed data transfer through the Thunderbolt interface and enhance interoperability between computers and external devices such as hard drives and monitors. Thunderbolt 3, initially compatible only with the MacBook Pro, later became universal and compatible with the USB-C interface, significantly expanding the range of applications for Thunderbolt devices. These devices benefit from faster transfer speeds, bidirectional data transfer, and the ability to daisy-chain multiple devices without a separate power source, minimizing clutter and maximizing usability.
What is the difference between USB-C and Thunderbolt?
Thunderbolt is faster than USB-C and is clearly the better choice for data transfer. It also provides more power, but this is not necessary for most charging applications.
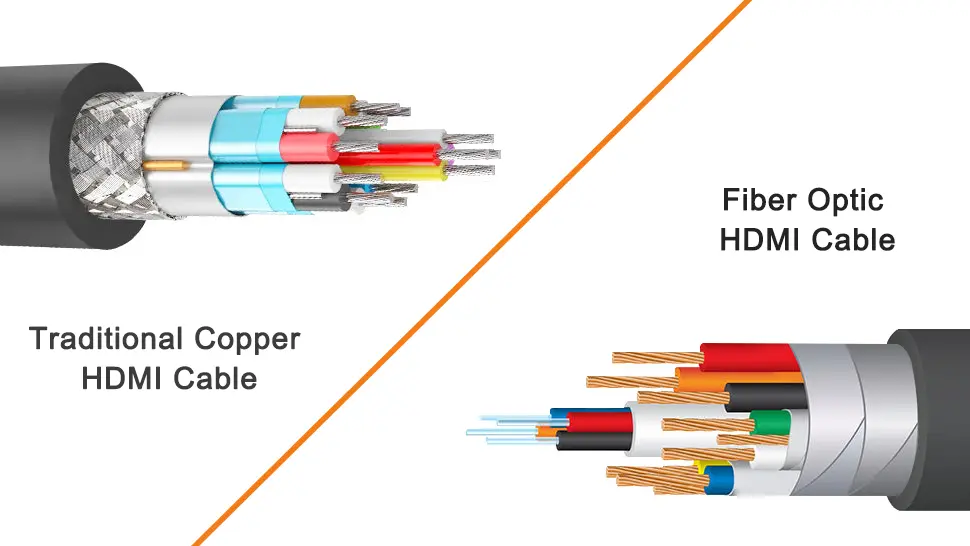
Thunderbolt and USB-C interfaces use the same USB-C connector, making them appear similar. However, Thunderbolt transfers more information at a faster speed. Thunderbolt 3 offers twice the capacity of Thunderbolt 2, with four PCI Express general-purpose data lanes and four DisplayPort video data lanes.
Thunderbolt 4 retains its predecessor's maximum data transfer speed of 40Gbit/s, four times faster than USB 3.2 Gen 2. In addition to daisy-chaining, it also adds support for dual 4K displays, security enhancements, and Thunderbolt Alternate Mode for USB hubs.
If you're building a computer system, choose Thunderbolt 4 or Thunderbolt 5 connections whenever possible for fast and stable data transfers. Whether you're connecting devices to transfer files or stream videos, Thunderbolt 5 is essential.
Thunderbolt 5 offers up to 80Gbit/s of bidirectional bandwidth, effectively doubling the performance of Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4.

How do you tell the difference between USB-C and Thunderbolt ports?
Distinguishing between USB-C and Thunderbolt ports can be difficult because not all devices clearly label them. While a Thunderbolt port may sometimes feature a lightning symbol, this isn't a guarantee.
To accurately identify a port, it's wise to:
● Check the product specifications: Consult the packaging, the manufacturer's website, or the device documentation to confirm the port type.
● Check the cable: Some Thunderboltcables feature a lightning symbol, but this isn't always the case.
Note that many devices, especially laptops, may have both USB-C and Thunderbolt ports, with different symbols indicating their functions. Be sure to carefully read the documentation to ensure you're using the correct cable and port to take advantage of Thunderbolt™'s enhanced capabilities.
Should you choose Thunderbolt or USB-C?
For most users, USB-C is sufficient for typical needs such as connecting accessories, storage devices, and charging. However, Thunderbolt is a better choice if you need:
● Fast transfer of large amounts of data
● Daisy-chaining multiple 4K displays and connecting multiple devices, emphasizing the ability to simplify your setup with fewer cables
● Using a Thunderbolt docking station
● Connecting numerous peripherals for gaming or other demanding tasks
Daisy-chaining not only supports high-resolution displays but also allows you to connect multiple devices using a single Thunderbolt cable, significantly reducing workspace clutter. This is especially useful for creative professionals working with multiple displays and storage devices.
Thunderbolt excels at quickly transferring large files like videos to external drives, which is useful for data backup and video editing workflows. Its ability to drive multiple 4K displays, providing higher video bandwidth, makes it ideal for graphic design and 3D modeling.
However, Thunderbolt's added features come at a price, and most budget PCs and devices don't support Thunderbolt. Consider whether the advantages are worth the extra cost. If you primarily use your computer for basic tasks like web browsing, email, and document editing, a USB-C port may be sufficient.

 USB C Docking & Hub
USB C Docking & Hub USB C Docking Station
USB C Docking Station USB C Hub-H Series
USB C Hub-H Series USB C Hub-H Series High End
USB C Hub-H Series High End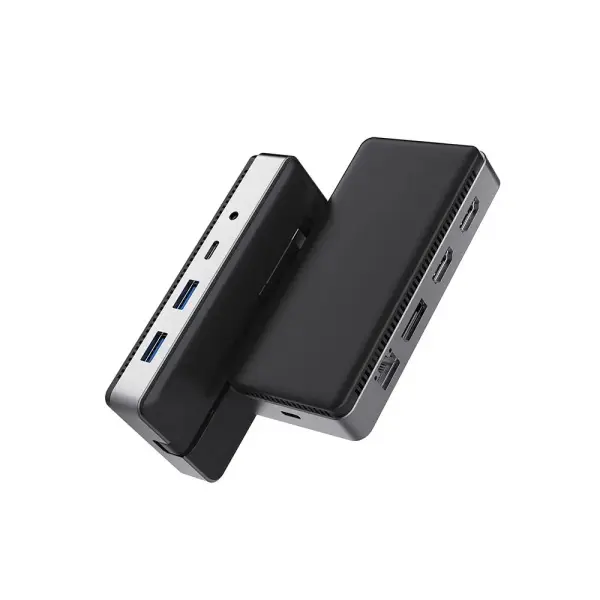 USB C Hub-X Series High End
USB C Hub-X Series High End HDMI Cable
HDMI Cable 4K HDMI Cable
4K HDMI Cable 8K HDMI Cable
8K HDMI Cable 16K HDMI Cable
16K HDMI Cable AOC HDMI Cable
AOC HDMI Cable HDMI Conversion Cable
HDMI Conversion Cable 8K DisplayPort Cable
8K DisplayPort Cable 16K DisplayPort Cable
16K DisplayPort Cable DisplayPort Conversion Cable
DisplayPort Conversion Cable XLR Cable
XLR Cable VGA Cable
VGA Cable DVI Cable
DVI Cable Type C To HDMI
Type C To HDMI Type C to DP
Type C to DP Type C to DVI
Type C to DVI Type C Adapter
Type C Adapter USB A to C Cable
USB A to C Cable USB C to C Cable
USB C to C Cable Micro USB Cable
Micro USB Cable USB4 Cable
USB4 Cable