Understanding Fiber Optic HDMI Cables
In today's digital age, high-definition audio and video equipment has become an integral part of our lives. From home theaters to game consoles, HDTVs to projectors, we have increasingly high demands for the quality and stability of audio and video transmission. HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface), currently the most mainstream audio and video transmission interface, is experiencing continuous evolution and improvement in cable performance. The emergence of fiber-optic HDMI cables has revolutionized high-definition transmission.
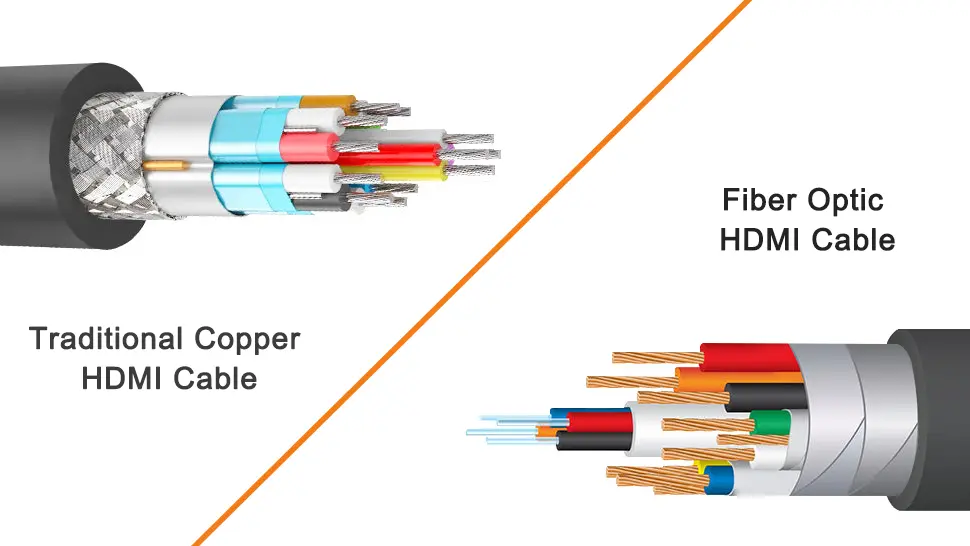
What is a fiber-optic HDMI cable?
A fiber-optic HDMI cable uses optical fiber technology to transmit high-definition audio and video data from one device to another. While traditional copper wires transmit electrical signals, fiber-optic technology conducts optical signals through thin, transparent wires made of glass or plastic.
How do fiber-optic HDMI cables work?
Fiber-optic HDMI cables use light or lasers to transmit data. Light pulses travel through tiny glass filaments, transmitting data. These filaments, due to their thinness, are able to transmit a large number of pulses. Converters are required at both ends to convert the optical signal to electrical and vice versa.
Fiber-optic HDMI cables have an optical-to-electrical conversion chip engine, requiring two optical-to-electrical conversion steps for signal transmission. The electrical signal is converted to an optical signal, which is then transmitted through the optical fiber line and then converted back to an electrical signal. The signal is efficiently transmitted from the Source terminal to the Display terminal.
Fiber Optic HDMI vs. Traditional (Copper) HDMI: Key Differences To Know
|
Feature |
Fiber Optic HDMI |
Traditional (Copper) HDMI |
Key Differences |
|
Signal Transmission |
Uses light signals. |
Uses electrical signals. |
Light is faster and doesn't degrade over long distances. |
|
Cable Length |
Handles 100+ feet easily without signal loss. |
Effective up to approximately 25 feet before weakening. |
Fiber optic cables are significantly better for long cable runs. |
|
Interference |
Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI). |
Susceptible to noise from nearby electrical devices. |
Fiber optic cables provide a cleaner signal without interference. |
|
Flexibility & Weight |
Lighter and more flexible. |
Generally less flexible and heavier. |
Fiber optic cables are easier to install in tight spaces and are less prone to putting stress on connectors. |
|
Price |
Generally, more expensive. |
Generally less expensive for shorter lengths. |
Fiber optic HDMI cables typically have a higher upfront cost. |
Advantages of Fiber Optic HDMI Cables
● Long-Distance Transmission: Thanks to the optical fiber transmission medium, fiber optic HDMI cables support long-distance transmission without signal loss. They can support signal transmission distances of 150 meters or more with minimal to no attenuation.
● Interference Resistance: Fiber optic HDMI cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can affect signal quality and stability. Copper HDMI cables may pick up noise from nearby power lines, routers, and other devices, especially over long distances, which can cause data loss.
● Lightweight and Flexible: Compared to copper cables of the same gauge, fiber optic HDMI cables are lighter and thinner. Their greater flexibility makes them easier to install. However, they are more susceptible to damage than copper cables.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic HDMI Cables
● Fragility: Compared to copper HDMI cables, fiber optic HDMI cables are more fragile and require careful handling and installation. Excessive bending, twisting, or excessive force can damage the optical fiber, resulting in signal loss or malfunction.
● Unidirectional: Fiber optic HDMI cables transmit audio and video in only one direction. They have designated input and output connectors and cannot be plugged in arbitrarily. Therefore, you must first identify the input and output connectors and connect them to the correct device or display port.
● Cost: Cost is another disadvantage of fiber optic HDMI cables; they are more expensive than regular HDMI cables.
HDMI Fiber Optic Cable Applications
Professional AV Systems: Ideal for conference rooms, auditoriums, and other professional venues requiring reliable, high-quality AV connectivity.
Home Theater: Ideal for setups where the signal source and display are far apart, such as projector systems or large home theater installations.
Digital Signage: Ensures clear and consistent signal transmission in large venues like airports, shopping malls, and stadiums.
Gaming and High-Resolution Displays: Supports the latest gaming consoles and high-resolution displays for an optimal visual experience.

 USB C Docking & Hub
USB C Docking & Hub USB C Docking Station
USB C Docking Station USB C Hub-H Series
USB C Hub-H Series USB C Hub-H Series High End
USB C Hub-H Series High End USB C Hub-X Series High End
USB C Hub-X Series High End HDMI Cable
HDMI Cable 4K HDMI Cable
4K HDMI Cable 8K HDMI Cable
8K HDMI Cable 16K HDMI Cable
16K HDMI Cable AOC HDMI Cable
AOC HDMI Cable HDMI Conversion Cable
HDMI Conversion Cable 8K DisplayPort Cable
8K DisplayPort Cable 16K DisplayPort Cable
16K DisplayPort Cable DisplayPort Conversion Cable
DisplayPort Conversion Cable XLR Cable
XLR Cable VGA Cable
VGA Cable DVI Cable
DVI Cable Type C To HDMI
Type C To HDMI Type C to DP
Type C to DP Type C to DVI
Type C to DVI Type C Adapter
Type C Adapter USB A to C Cable
USB A to C Cable USB C to C Cable
USB C to C Cable Micro USB Cable
Micro USB Cable USB4 Cable
USB4 Cable








